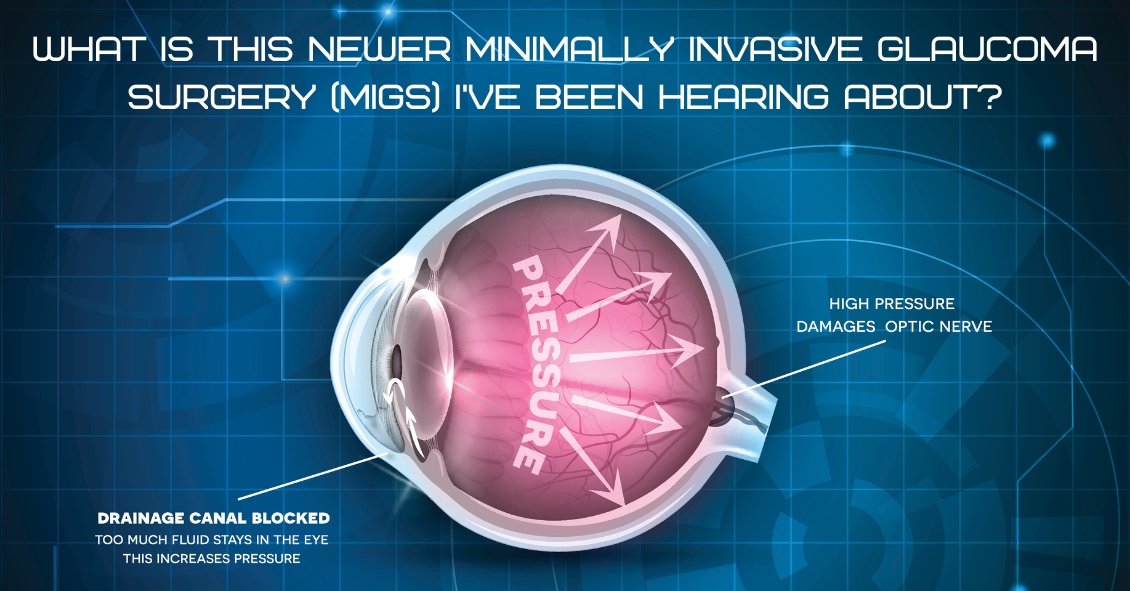
What to Do About Those Pesky Floaters
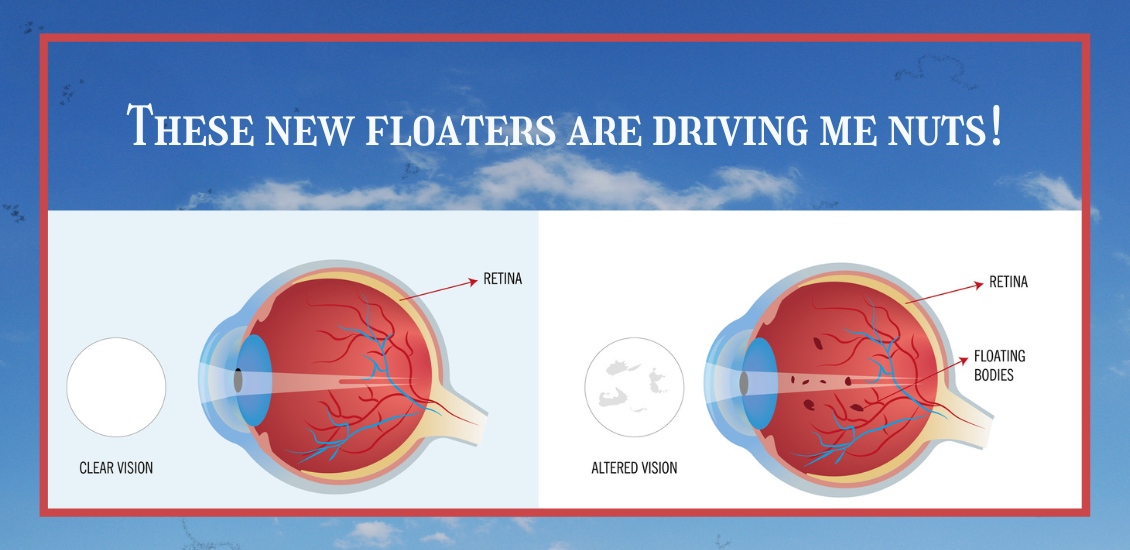
Do you have floaters in your vision?
Floaters are caused by thick areas in the gel-like fluid that fills the back cavity of your eye, called the vitreous.
Many people, especially highly near-sighted people, often see some degree of floaters for a good portion of their lives. Often, these floaters are in the periphery of your vision and may only be visible in certain lighting conditions. The most frequent conditions are when you are in bright sunlight and are looking toward the clear blue sky. I know this from personal experience since I have a floater in my left eye that I most often see when swimming outdoors. Every time I turn my head to the left to breathe I see this floater moving in my peripheral vision.
This is totally harmless other than when I’m swimming in the ocean and swear that sudden object in my peripheral vision is a shark bearing down on me. Some people who have floaters are not as lucky– the floater might be in their central vision and almost constantly […]