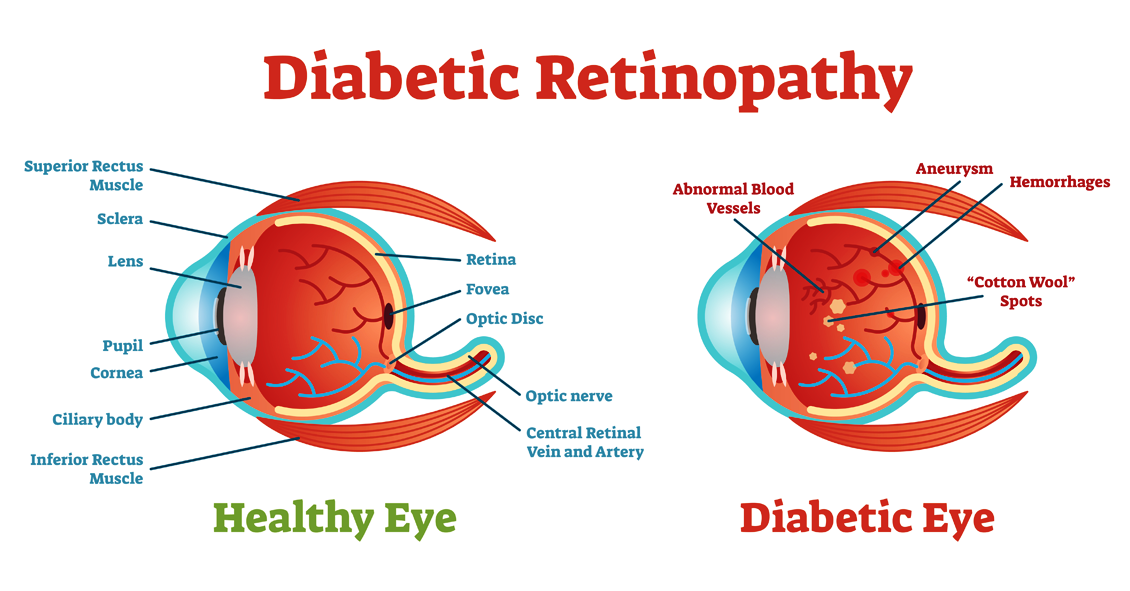
Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
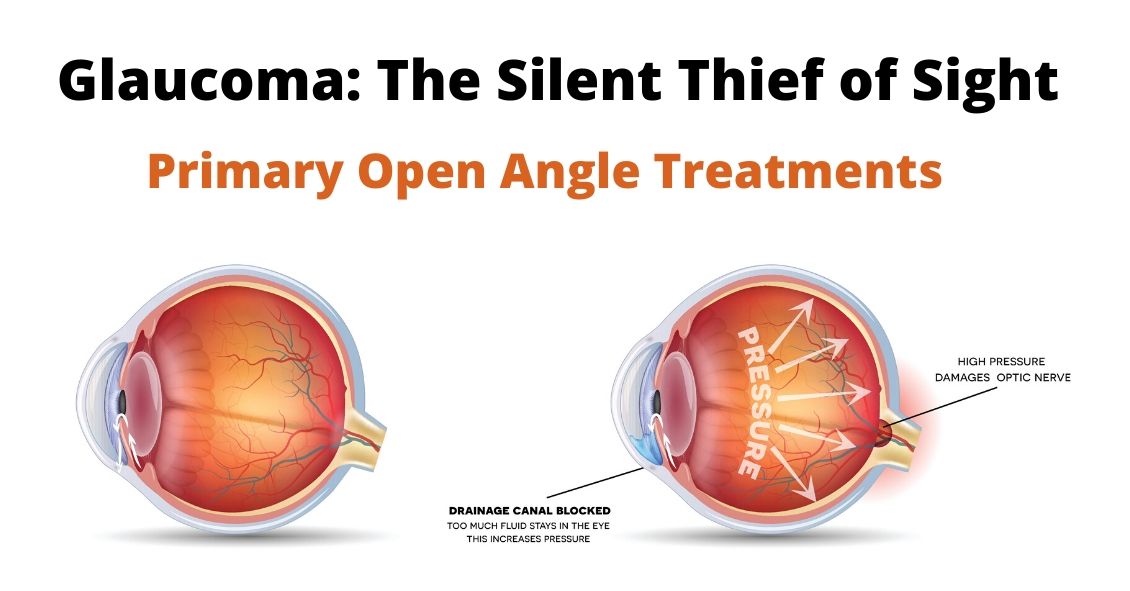
There are several different variations of Glaucoma, but in this article we will mainly focus on Primary Open Angle Glaucoma. This means that there is no specific underlying cause for the Glaucoma like inflammation, trauma, or a severe cataract. It also means that the drainage angle where fluid is drained from the inside of the eye into the bloodstream is not narrow or closed.
Closed or Narrow Angle Glaucoma, which will be discussed in another article, is treated differently from Open Angle Glaucoma
In the U.S., Primary Open Angle Glaucoma (POAG) is by far the most common type of Glaucoma we treat.
Glaucoma is a disease where the Optic Nerve in the back of the eye deteriorates over time, and that deterioration has a relationship to the Intraocular Pressure (IOP). Most – but not all – people diagnosed with Glaucoma have an elevated IOP. Some people have fairly normal IOP’s but show the characteristic deterioration in the Optic Nerve. Regardless of whether or not the pressure was high initially, our primary treatment is to lower the […]